The Digital Lending (R)evolution


Lending is a term used when a lender gives money to an individual or entity with a specific guarantee or based on the trust that the recipient will repay the borrowed money with certainly added gains, such as interest.
Evolution of Lending:
Lending dates back to Ancient Mesopotamia in 3000 BC. Farmers took seeds as loans, and they paid back their loans with their crops and fresh stock harvest. Ancient Greece was one of the earliest adopters of the concept of interest. The Greeks charged 12% on mortgages and larger loans, while small loans could go upto 18%. Plato (428BC – 348 BC) and Aristotle (384BC -322 BC) believed that usury (predatory lending) could lead to societal instability. Although religion influenced lending in the Middle Ages (500AD- 1500AD), it continued in some or the other form. The earliest banks with brick & mortar branches popped up in England around 1826 AD. Since qualifying for a loan was difficult, merchants and independent lenders were still the most popular options in the 19th century.
On the other hand, the Bank of North America began its operations in 1791 AD. Focussed on home loans and mortgage-backed loans, they lent heavily in the 1870s. Universal Credit Cards started being used in the 1950s by Diner’s Club Inc., while Visa and Mastercard were formed in the 1970s. Formal Banks led the charge significantly up until the Global Financial Crisis of 2008. The market crash allowed rapid digitisation of lending, enabling FinTechs to take centre stage.
The COVID-19 Pandemic acted as a thrust to the engine, propelling Digital Lending not only to be established as a viable alternative but the first choice. This also popularized the concept of Neo-banks and Payments Banks.
But, What is Digital Lending?
Digital Lending is a new-age process to offer loans/ credit services to credit-seeking customers by leveraging digital technology. It allows financial institutions to reach their customers far and wide.
Imagine you are a farmer residing in a rural region of India. You urgently require a small loan to buy a tractor to increase your workforce and cost-efficiency. Owing to the high Internet penetration, you have access to the Internet, but you do not have access to a physical bank branch in your vicinity. What do you do? Yes, you apply for a loan with just a tap on your phone. This is Digital Lending.
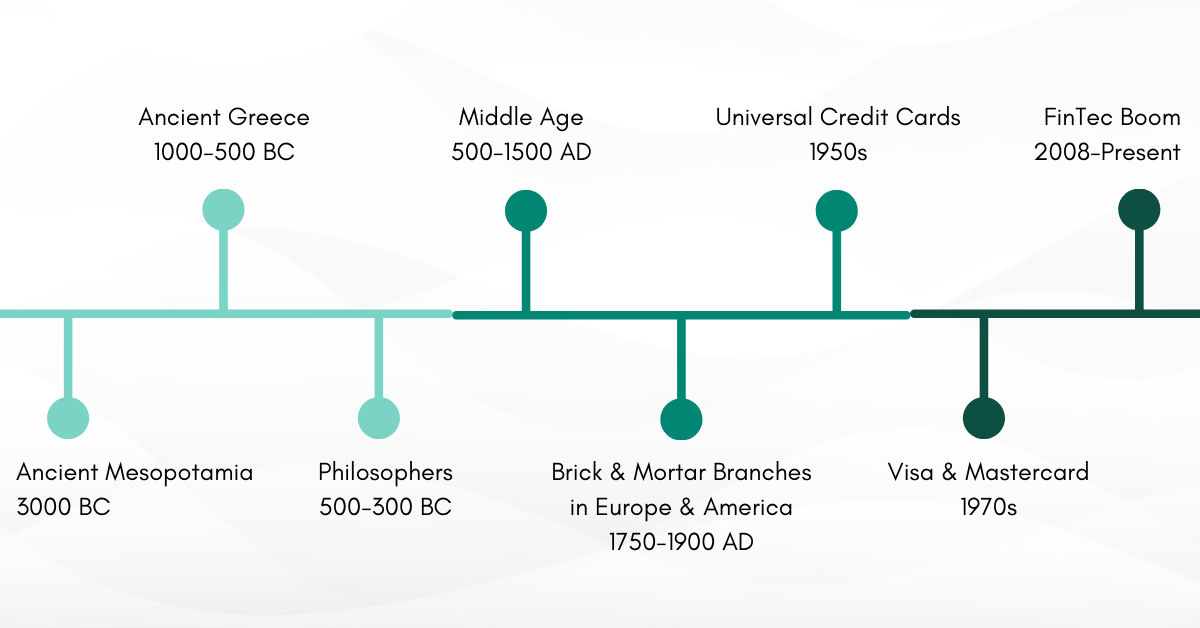
Evolution of Lending
Types of Digital Lending
1) Collaborative Model:
A collaboration between FinTechs and Traditional Banks provides a win-win situation for both parties.
For instance, SBM Bank has partnered with OneCard to launch a mobile-based credit card.
2) Independent Model:
A model that allows direct lending solutions for end customers without any partnerships can be called an independent model.
For example, LendingKart provides direct loans to SMEs.
3) POS Based Model:
This model uses POS Transaction data to create lending programs aimed at financing merchants who use POS machines and customers.
For example, PineLabs, in collaboration with ZestMoney, provides instant credit to customers at retail stores across the country by approving their credit limit based on Traditional and Alternative Data-based insights. It also includes BNPL as a service. On the other hand, NeoGrowth provides small and medium unsecured loans to merchants.
4) Aggregator Model:
It focuses on providing the end consumer with different lending options available in the market based on the exact need (tenure, amount, prepayment mode, etc.) of the consumer. For example, aggregators like PaisaBazaar and Lendio have an aggregator model.
5) Peer-To-Peer Model:
It aims to meet borrowers’ demands through other individuals willing to deploy their liquid funds for lending purposes.
For instance, Faircent allows direct peer-to-peer lending for individuals.
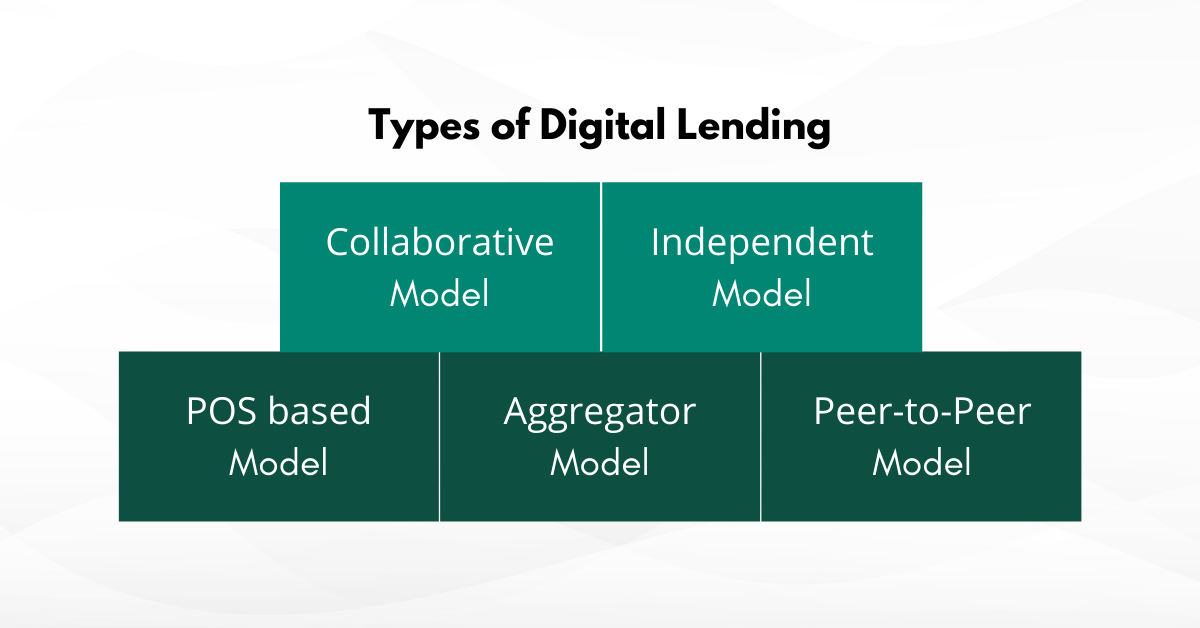
Types of Digital Lending
Head To Head: Traditional Lending vs. Digital Lending
Application:
From filling out never-ending application forms to submitting several supporting documents, applying for Traditional Loans is tedious.
One can skip long lines at the branch and complete the entire process online, saving time and effort if they choose a Digital Loan.
Documentation:
A time-consuming task, Traditional Loans involve filling out forms, showing references, photocopies, and attested paperwork.
For digital loans, one needs to upload only a few essential documents like address proof and identity proof for e-KYC. Loans are granted much faster in the latter.
Disbursal Time:
Traditional Banks can take weeks, even months, to disburse loans. Long disbursal time might be disadvantageous for small business owners who might need instant loans. On the other hand, Digital Lenders process loans within hours, and the funds reach one’s account within 2 to 4 working days.
Eligibility:
Factors like employment history, current income, assets, liabilities and credit score are considered. Only considering these factors might restrict the eligibility to only a fragment of the credit-seeking individuals.
Although Digital Lenders consider the conventional factors mentioned above, they also look at Alternative data parameters like education levels, professional background and potential future earnings to determine eligibility.
Technology:
In traditional banks, old and clunky systems, confusing UI and poor consumer tech support for queries leave customers with a sour taste. A seamless, intuitive and clean UI and a functionally superior experience make digital lending applications a go-to choice.
Can Alternative Data help optimise Digital Lending?
As a digital lender, reaching the right customer group to disburse loans is imperative. While digital loans are faster, more convenient, and easier to obtain, we also see drawbacks.
Digital lending depends heavily on technology and the Internet. One point of failure can bring the entire system to a halt. Secondly, lesser human-to-human interaction can cause a drop in the customer experience.
The third problem is over-indebtedness. The ease of borrowing a loan can also be seen as a disadvantage in the long run. Since automation plays such an essential part in online lending platforms, many customers who are approved for a loan will ultimately have difficulty paying it back. The algorithms rely heavily on data, not just voluminous chunks of ambiguous data but structured data. This structured data can allow digital lenders to build optimised models to provide more accurate insights.
Alternative Data can provide digital lenders to create unique scorecards to understand customers better. Alt Data can further deep dive into ‘people’ data to analyse customers and track their loan repayment cycle. This can allow digital lenders to estimate the delinquency of a person even before their loan is approved!
Thus, this can reduce delinquency rates and cause a significant drop in non-performing assets. A substantial increase in loan book size and a surge in efficiency are the direct benefits for Digital Lenders. Indian banks are fast adapting to these new technologies by redesigning their strategies to maximise their gains.
Key Takeaways:
- Lending started in Mesopotamia in 3000 BC, and it has come a long way since, changing forms of repayment and modes of service according to the evolving times.
- Digital Lending is the digital, software-driven loan disbursal to credit-seeking customers.
- It requires less application time, disbursal time, and minimal documentation and provides a broader customer base and robust technology.
- There are five types of lending: Collaborative, Independent, POS Transaction-based, Aggregator and P2P lending.
- Digital Lending is better than Traditional Lending as it allows easy application, documentation and faster disbursement and leverages technology.
- Alternate Data can allow Digital Lenders to enrich their decision-making by predicting delinquency.
Looking to sustainably increase your Loan Book Size ? We have a solution!